Copied from http://www.westseattleherald.com/2015/02/27/news/32-acres-land-myers-way-subject-meeting-save-it
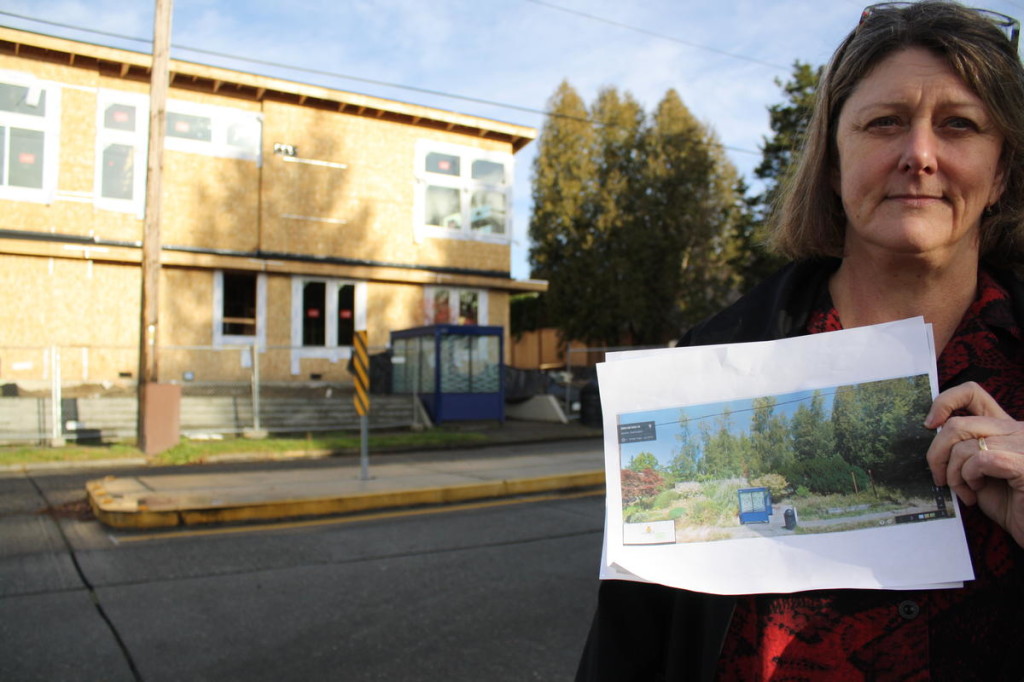
A community meeting aimed at preserving 32 acres of land on Myers Way South is set for March 14. Organizers say that they need to reach the threshold of 500 people who choose to keep that land undeveloped, and eventually for it to become “Discovery Park South”, otherwise they say it could be sold for the possible site of a Lowes Hardware Store.
Information from the organizers
The City of Seattle intends to sell the Myers Parcels for commercial development soon, most likely to LOWES. Seattle Parks has indicated it does not want it. If 500 people say they want it to become Discovery Park South, they will reconsider.
WHAT: Myers Parcels occupy 32 acres of undeveloped surplus land owned by the City of Seattle It is steep, wooded slopes, wetlands, and a meadow.
WHERE: The land is located in south and east end of West Seattle, between White Center and Highland Park. It is adjacent and south of the Joint Training Facility, 9401 Myers Way South and Arrowhead senior housing.
CONTACT: Cass Turnbull: cassturnbull@comcast.net or 206-783-9093
HELP: Send an email to the Mayor and/or your councilmember saying you want Myers Parcels saved as Myers Park, a natural area.
COME: You are invited to come to the first ever gathering of SAVE MYERS PARK, on Saturday March 14th, 10-noon, at the offices of the Duwamish River Cleanup Coalition, 210 S. Hudson.
Call or email Cass to confirm and for questions. 206-783-9093. Or email cassturnbull@comcast.net.
The story of the Myers Parcels:
By Cass Turnbull
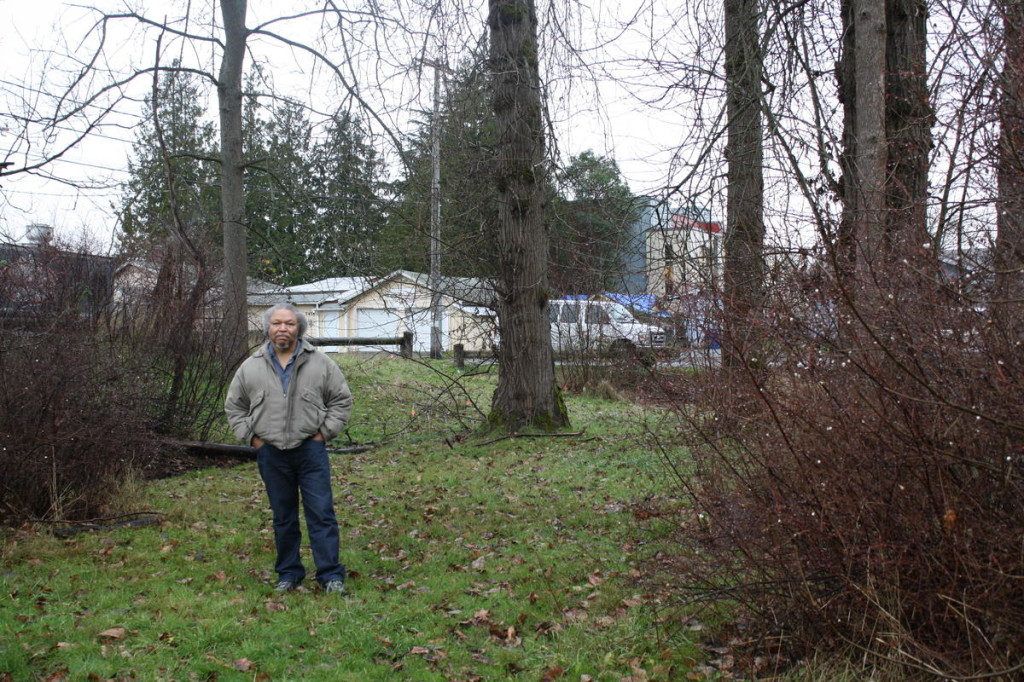
The Myers parcels may be the last large, undeveloped piece of property that could become a major park in Seattle. It is 32 acres of surplus land already owned by the City. It is located at the south border of West Seattle, between White Center and South Park. It is an easily ignored piece of land, it seems remote from the industry, the homes, and certainly from the building boom that is elsewhere. You can see 509 from it and it is surrounded, and locked up entirely, by a chain link fence. You might not even notice it when driving north to get to the 1st Ave Bridge.
I noticed it because it has woods, fields and as I found out, water. And because of my work on the Save Our Substations project I knew it was City owned surplus land. After researching its history I can say that Myers is a much abused piece of God’s green earth. For most of its modern history it was mined as a gravel pit. Nintendo owned it for a while and insisted that Seattle buy all 50 acres of the property if they wanted to buy any of it. The best piece, the centrally located flatland, became Seattle’s interdepartmental Joint Training Facility.
Then in 2007, just before the great recession, the rest of the land was put up for sale by the Council. The City wanted to pay off an interdepartmental loan on the land and stimulate the economy in underserved south Seattle. For various reasons the deal with LOWES flipped.
Development has recently begun to nibble at the corners. The property just adjacent to the North has become a spiffy new building complex for retired people. Above the steep cliff and to the west the King County Housing, people decided to turn over large swaths of their land to build Greenbridge, which is the latest thing in mixed use housing designed to deal with Seattle’s affordable housing problem. The steep greenbelt to the north of the retirement complex got taken by parks as part of the Westcrest Park, thank God. It extends the Duwamish greenbelt to, you know, Myers. On the east side of Myers Way, located behind an inconspicuous hole in the chain link fence, is a trail going down the steep wooded hill to SR 509. A homeless camp is hidden there that has been beautifully landscaped and cleaned by its members.
As for Myers proper, the Firemen decided they needed to build their own dream training facility (for $33 million of your tax dollars, about the price of the entire pieces of land). A local environmental hero, John Beal, fought to stop the development because Myers feeds Hamm creek, one of the tributaries of the Duwamish. He had spent 22 years of his life restoring the Hamm. Some say that losing the battle against the training facility caused the heart attack that killed him shortly thereafter. Seattle was fined, but the construction continued and was finished. Now you can see the center. You can’t enter the Firefighter’s facility itself, its security gated and fenced, but sometimes you can see pink smoke arising from a concrete tower. From Google Earth you can see roads lined in big red tucks. A tiny duck pond at the visitors parking area is what remains of the wetland.
Money is always the problem. The State Accountancy Act says you can’t just give or transfer property from one department to the other. I’m investigating several possible ‘work-arounds’ to make the land affordable, or perhaps even free. I applied for grants to create a think tank of a lawyer, a strategist, and policy analyzer to check out the feasibility of various possible options. Now we need a coalition of supporters to build momentum to save the property.
The kids of future Seattle will not have what I had as a girl growing up in Seattle. Because of the avalanche of density headed our way, there just won’t be the backyards, the vacant lots and the empty campgrounds of my youth. Exploring the vacant lot next door is how I came to love nature. I want the kids of Greenbridge to be able to bike to Myers Park to climb trees, build forts, play in mud, and pretend they are in some distant wild place. I want a place where there are frogs to hear, crickets to catch, a killdeer and swifts to watch, or perhaps even a salmon spawning.